16. Tree
Traversal
Problem 1: Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Leetcode:94)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Explanation:
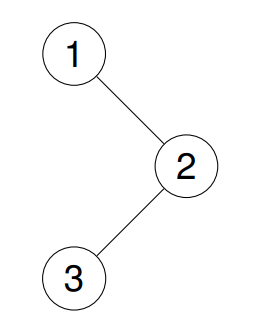
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,2,6,5,7,1,3,9,8]
Explanation:
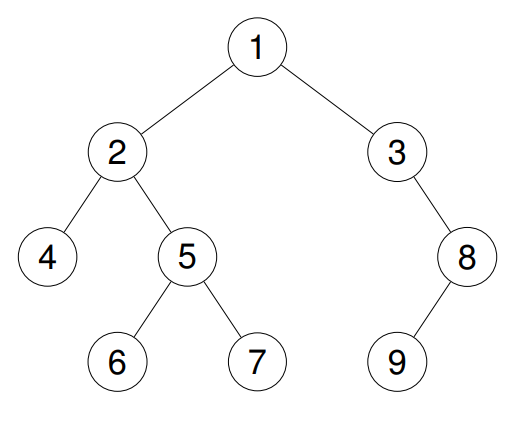
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Binary Tree Preorder Traversal (Leetcode:144)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [1,2,3]
Explanation:

Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [1,2,4,5,6,7,3,8,9]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Binary Tree Postorder Traversal (Leetcode:145)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:

Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,6,7,5,2,9,8,3,1]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Binary Tree Level Order Traversal (Leetcode:102)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000].
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal (Leetcode:103)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Code and Explaination
Problem 6: Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II (Leetcode:107)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000].
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Code and Explaination
Problem 7: Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree (Leetcode:987)
Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, calculate the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
For each node at position (row, col), its left and right children will be at positions (row + 1, col - 1) and (row + 1, col + 1) respectively. The root of the tree is at (0, 0).
The vertical order traversal of a binary tree is a list of top-to-bottom orderings for each column index starting from the leftmost column and ending on the rightmost column. There may be multiple nodes in the same row and same column. In such a case, sort these nodes by their values.
Return the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
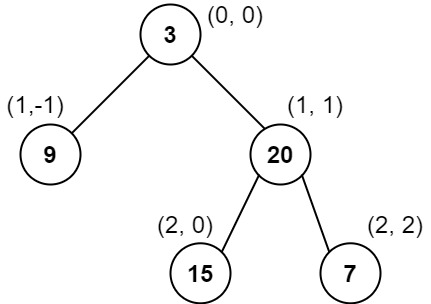
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -1: Only node 9 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 3 and 15 are in this column in that order from top to bottom.
Column 1: Only node 20 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 2:
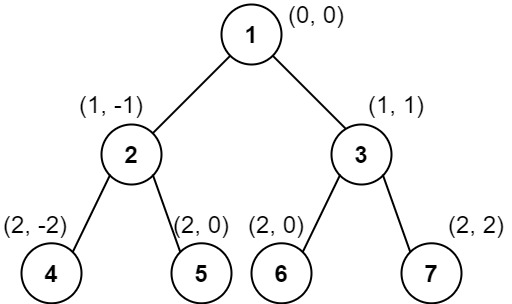
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -2: Only node 4 is in this column.
Column -1: Only node 2 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 1, 5, and 6 are in this column.
1 is at the top, so it comes first.
5 and 6 are at the same position (2, 0), so we order them by their value, 5 before 6.
Column 1: Only node 3 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 3:
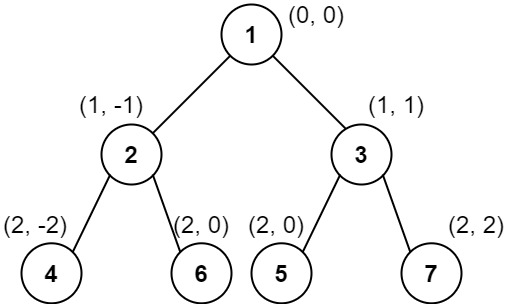
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
This case is the exact same as example 2, but with nodes 5 and 6 swapped.
Note that the solution remains the same since 5 and 6 are in the same location and should be ordered by their values.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000].
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Code and Explaination
Build Understanding
Problem 1: Invert Binary Tree (Leetcode:226)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Binary Tree Tilt (Leetcode:563)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Diameter of Binary Tree (Leetcode:543)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Merge Two Binary Trees (Leetcode:617)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Minimum Depth of Binary Tree (Leetcode:111)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 6: Balanced Binary Tree (Leetcode:110)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 7: Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (Leetcode:104)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 9: Symmetric Tree (Leetcode:101)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Binary Search Trees
Problem 1: Search in a Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:700)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Minimum Absolute Difference in BST (Leetcode:530)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Range Sum of BST (Leetcode:938)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Delete Node in a BST (Leetcode:450)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 6: Trim a Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:669)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 7: Insert into a Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:701)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 8: Kth Smallest Element in a BST (Leetcode:230)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 9: All Elements in Two Binary Search Trees (Leetcode:1305)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 10: Binary Search Tree Iterator (Leetcode:173)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 11: Binary Search Tree to Greater Sum Tree (Leetcode:1038)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 12: Maximum Sum BST in Binary Tree (Leetcode:1373)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Path
Problem 1: Binary Tree Paths (Leetcode:257)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Path Sum II (Leetcode:113)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Sum Root to Leaf Numbers (Leetcode:129)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum (Leetcode:124)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 6: Path Sum III (Leetcode:437)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 7: Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree (Leetcode:1457)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
construct a binary tree/BST
Problem 1: Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal (Leetcode:105)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal (Leetcode:106)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Postorder Traversal (Leetcode:889)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:108)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal (Leetcode:1008)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
View Problem
Problem 1: Binary Tree Right Side View (Leetcode:199)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Lowest Common Ancestor
Problem 1: Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (Leetcode:236)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:235)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Lowest Common Ancestor of Deepest Leaves (Leetcode:1123)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Validate Trees
Problem 1: Validate Binary Tree Nodes (Leetcode:1361)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Validate Binary Search Tree (Leetcode:98)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
miscellaneous
Problem 1: Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List (Leetcode:114)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 2: Count Complete Tree Nodes (Leetcode:222)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 3: Maximum Width of Binary Tree (Leetcode:662)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 4: Check Completeness of a Binary Tree (Leetcode:958)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 5: Cousins in Binary Tree (Leetcode:993)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 6: Maximum Difference Between Node and Ancestor (Leetcode:1026)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 7: Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs (Leetcode:1530)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 8: Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes (Leetcode:865)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 9: All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree (Leetcode:863)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 10: Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree (Leetcode:1379)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 11: All Possible Full Binary Trees (Leetcode:894)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 12: Delete Leaves With a Given Value (Leetcode:1325)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 13: Delete Nodes And Return Forest (Leetcode:1110)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 14: Find Duplicate Subtrees (Leetcode:652)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 15: House Robber III (Leetcode:337)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 16: Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another (Leetcode:2096)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 17: Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II (Leetcode:117)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 18: Distribute Coins in Binary Tree (Leetcode:979)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 19: Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree (Leetcode:297)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination
Problem 20: Binary Tree Cameras (Leetcode:968)
Problem Statement
Code and Explaination





