19. Tries
Problem 1: Implement Trie (Prefix Tree) (Leetcode:208)
Problem Statement
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto the trie.boolean search(String word)Returnstrueif the stringwordis in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), andfalseotherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returnstrueif there is a previously inserted stringwordthat has the prefixprefix, andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000wordandprefixconsist only of lowercase English letters.- At most
3 * 104calls in total will be made toinsert,search, andstartsWith.
Problem 2: Longest Word in Dictionary (Leetcode:720)
Problem Statement
Given an array of strings words representing an English Dictionary, return the longest word in words that can be built one character at a time by other words in words.
If there is more than one possible answer, return the longest word with the smallest lexicographical order. If there is no answer, return the empty string.
Note that the word should be built from left to right with each additional character being added to the end of a previous word.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["w","wo","wor","worl","world"]
Output: "world"
Explanation: The word "world" can be built one character at a time by "w", "wo", "wor", and "worl".
Example 2:
Input: words = ["a","banana","app","appl","ap","apply","apple"]
Output: "apple"
Explanation: Both "apply" and "apple" can be built from other words in the dictionary. However, "apple" is lexicographically smaller than "apply".
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 10001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.
Problem 3: Map Sum Pairs (Leetcode:677)
Problem Statement
Design a map that allows you to do the following:
- Maps a string key to a given value.
- Returns the sum of the values that have a key with a prefix equal to a given string.
Implement the MapSum class:
MapSum()Initializes theMapSumobject.void insert(String key, int val)Inserts thekey-valpair into the map. If thekeyalready existed, the originalkey-valuepair will be overridden to the new one.int sum(string prefix)Returns the sum of all the pairs' value whosekeystarts with theprefix.
Example 1:
Input
["MapSum", "insert", "sum", "insert", "sum"]
[[], ["apple", 3], ["ap"], ["app", 2], ["ap"]]
Output
[null, null, 3, null, 5]Explanation
MapSum mapSum = new MapSum();
mapSum.insert("apple", 3);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 3 (apple = 3)
mapSum.insert("app", 2);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 5 (apple + app = 3 + 2 = 5)
Constraints:
1 <= key.length, prefix.length <= 50keyandprefixconsist of only lowercase English letters.1 <= val <= 1000- At most
50calls will be made toinsertandsum.
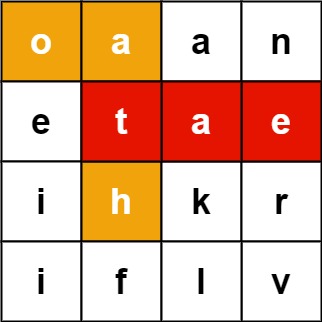
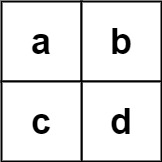
Problem 4: Word Search II (Leetcode:212)
Problem Statement
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Example 1:
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
Example 2:
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output: []
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
Problem 5: Replace Words (Leetcode:648)
Problem Statement
In English, we have a concept called root, which can be followed by some other word to form another longer word - let's call this word derivative. For example, when the root "help" is followed by the word "ful", we can form a derivative "helpful".
Given a dictionary consisting of many roots and a sentence consisting of words separated by spaces, replace all the derivatives in the sentence with the root forming it. If a derivative can be replaced by more than one root, replace it with the root that has the shortest length.
Return the sentence after the replacement.
Example 1:
Input: dictionary = ["cat","bat","rat"], sentence = "the cattle was rattled by the battery"
Output: "the cat was rat by the bat"
Example 2:
Input: dictionary = ["a","b","c"], sentence = "aadsfasf absbs bbab cadsfafs"
Output: "a a b c"
Constraints:
1 <= dictionary.length <= 10001 <= dictionary[i].length <= 100dictionary[i]consists of only lower-case letters.1 <= sentence.length <= 106sentenceconsists of only lower-case letters and spaces.- The number of words in
sentenceis in the range[1, 1000]- The length of each word in
sentenceis in the range[1, 1000]- Every two consecutive words in
sentencewill be separated by exactly one space.sentencedoes not have leading or trailing spaces.
Problem 6: Add and Search Word (Leetcode:211)
Problem Statement
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary()Initializes the object.void addWord(word)Addswordto the data structure, it can be matched later.bool search(word)Returnstrueif there is any string in the data structure that matcheswordorfalseotherwise.wordmay contain dots'.'where dots can be matched with any letter.
Example:
Input
["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search"]
[[],["bad"],["dad"],["mad"],["pad"],["bad"],[".ad"],["b.."]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,false,true,true,true]
Explanation
WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
wordDictionary.addWord("bad");
wordDictionary.addWord("dad");
wordDictionary.addWord("mad");
wordDictionary.search("pad"); // return False
wordDictionary.search("bad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search("b.."); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length <= 25wordinaddWordconsists of lowercase English letters.wordinsearchconsist of'.'or lowercase English letters.- There will be at most
2dots inwordforsearchqueries.- At most
104calls will be made toaddWordandsearch.
Problem 7: Word Break (Leetcode:139)
Problem Statement
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, return true if s can be segmented into a space-separated sequence of one or more dictionary words.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leetcode", wordDict = ["leet","code"]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because "leetcode" can be segmented as "leet code".
Example 2:
Input: s = "applepenapple", wordDict = ["apple","pen"]
Output: true
Explanation: Return true because "applepenapple" can be segmented as "apple pen apple".
Note that you are allowed to reuse a dictionary word.
Example 3:
Input: s = "catsandog", wordDict = ["cats","dog","sand","and","cat"]
Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 3001 <= wordDict.length <= 10001 <= wordDict[i].length <= 20sandwordDict[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordDictare unique.
Problem 8: Maximum XOR of Two Numbers in an Array (Leetcode:421)
Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums, return the maximum result of nums[i] XOR nums[j], where 0 <= i <= j < n.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8]
Output: 28
Explanation: The maximum result is 5 XOR 25 = 28.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [14,70,53,83,49,91,36,80,92,51,66,70]
Output: 127
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1050 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
Problem 9: Search Suggestions System (Leetcode:1268)
Problem Statement
You are given an array of strings products and a string searchWord.
Design a system that suggests at most three product names from products after each character of searchWord is typed. Suggested products should have common prefix with searchWord. If there are more than three products with a common prefix return the three lexicographically minimums products.
Return a list of lists of the suggested products after each character of searchWord is typed.
Example 1:
Input: products = ["mobile","mouse","moneypot","monitor","mousepad"], searchWord = "mouse"
Output: [["mobile","moneypot","monitor"],["mobile","moneypot","monitor"],["mouse","mousepad"],["mouse","mousepad"],["mouse","mousepad"]]
Explanation: products sorted lexicographically = ["mobile","moneypot","monitor","mouse","mousepad"].
After typing m and mo all products match and we show user ["mobile","moneypot","monitor"].
After typing mou, mous and mouse the system suggests ["mouse","mousepad"].
Example 2:
Input: products = ["havana"], searchWord = "havana"
Output: [["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"],["havana"]]
Explanation: The only word "havana" will be always suggested while typing the search word.
Constraints:
1 <= products.length <= 10001 <= products[i].length <= 30001 <= sum(products[i].length) <= 2 * 104- All the strings of
productsare unique.products[i]consists of lowercase English letters.1 <= searchWord.length <= 1000searchWordconsists of lowercase English letters.
Problem 10: Count Prefixes of a Given String (Leetcode:2255)
Problem Statement
You are given a string array words and a string s, where words[i] and s comprise only of lowercase English letters.
Return the number of strings in words that are a prefix of s.
A prefix of a string is a substring that occurs at the beginning of the string. A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["a","b","c","ab","bc","abc"], s = "abc"
Output: 3
Explanation:
The strings in words which are a prefix of s = "abc" are:
"a", "ab", and "abc".
Thus the number of strings in words which are a prefix of s is 3.
Example 2:
Input: words = ["a","a"], s = "aa"
Output: 2
Explanation:
Both of the strings are a prefix of s.
Note that the same string can occur multiple times in words, and it should be counted each time.
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 10001 <= words[i].length, s.length <= 10words[i]andsconsist of lowercase English letters only.
Problem 11: K-th Smallest in Lexicographical Order (Leetcode:440)
Problem Statement
Given two integers n and k, return the kth lexicographically smallest integer in the range [1, n].
Example 1:
Input: n = 13, k = 2
Output: 10
Explanation: The lexicographical order is [1, 10, 11, 12, 13, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], so the second smallest number is 10.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 1
Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 109
Problem 12: Palindrome Pairs (Leetcode:336)
Problem Statement
You are given a 0-indexed array of unique strings words.
A palindrome pair is a pair of integers (i, j) such that:
0 <= i, j < words.length,i != j, andwords[i] + words[j](the concatenation of the two strings) is a palindrome.
Return an array of all the palindrome pairs of words.
You must write an algorithm with O(sum of words[i].length) runtime complexity.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["abcd","dcba","lls","s","sssll"]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[3,2],[2,4]]
Explanation: The palindromes are ["abcddcba","dcbaabcd","slls","llssssll"]
Example 2:
Input: words = ["bat","tab","cat"]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0]]
Explanation: The palindromes are ["battab","tabbat"]
Example 3:
Input: words = ["a",""]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0]]
Explanation: The palindromes are ["a","a"]
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 50000 <= words[i].length <= 300words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.